Maths kit
Maths resource material for primary classes (1st to 5th )
When students come to school he came with a lot of knowledge into school , at school to understand child properly need to assess certain competencies , we can call the pre-primary learning outcomes ,here I share learning outcome at pre – primary stages:-
Aims of Preschool Education
Providing strong foundation for all round development and lifelong learning.
Preparing the child for school.
Guiding principles for Preschool Curriculum
Learning is a continuous and cumulative.
Evidence from neuroscience proves that early learning matters for later outcomes.
Each child is different and grows, learns and develops at her/his own pace.
Play and activity are the primary context of learning and development.
Responsive and supportive interactions with adults are essential to children’s learning.
Children learn by being provided the environment for experiential learning.
Interactive teaching enhances learning experiences.
Development and use of indigenous material enhances learning opportunities.
Responsive to the context and appreciation of diversity support learning.
Mother tongue /Home language should be the medium of instruction.
Family involvement contribute to learning.
Goals of Preschool Education
Children maintain good health and wellbeing
Children become effective communicators
Children become involved learners and connect with their immediate environment
Pedagogy
Learning Outcome
Age 3-5 years
There is no specific maths outcome , learning is totality. In Goal 3 –Children become involved learners and connect with their immediate environment.
Sensory Development
Sight
Sound
Touch
Smell
Taste
Cognitive skills
Observation
Identification
Memory
Matching
Classification
Patterns
Sequential thinking
Critical thinking
Creative thinking
Problem solving
Reasoning
Curiosity
Experimentation
Exploration
Concept formation
Colour ,shapes, Distance, Measurement ,Size, Length, Weight ,Height , Time
Spatial Sense
One to one correspondence
Number Sense
Count and tell how many
Numeral recognition
Sense of order ( can count ahead of a number up to 10)
Strat from here how should be class of 1st grade in physically , pedagogically and what should be learning outcome at this stage ? Pragya classes seems in continuation of pre schooling, rich physical environment , activity based and group based pedagogy. Here what are the suggestive teaching learning resource material in class 1st and 2nd and for 3rd ,4th,5th ?
class-wise Learning outcomes
Class I
The learner
• classifies objects into groups based on a few physical attributes, such as shape, size and other observable properties including rolling and sliding recites number names and counts objects up to 20, concretely, pictorially and symbolically
• works with numbers 1 to 20
––counts objects using numbers 1 to 9
––compares numbers up to 20. For example, tell whether number of girls or number of boys is more in the class
• applies addition and subtraction of numbers 1 to 20 in daily life
––constructs addition facts up to 9 by using concrete objects.
For example to find 3+3 counts 3 steps forward from 3 and concludes that 3+3=6
––subtracts numbers using 1 to 9. For example the child takes out 3 objects from a collection of 9 objects and counts the remaining to conclude 9-3=6
––solves day-to-day problems related to addition and subtraction of numbers up to 9
• recognises numbers up to 99 and writes numerals
• describes the physical features of various solids/shapes in her own language. For example, a ball rolls, a box slides etc.
• estimates and measures short lengths using non-uniform units like a finger, hand span, length of a forearm, footsteps, etc.
• observes, extends and creates patterns of shapes and numbers. For example, arrangement of shapes/objects/ numbers, etc.
––1,2,3,4,5,…
––1,3,5,…
––2,4,6,…
––1,2,3,1,2,…, 1,…3,…
• collects, records (using pictures/numerals) and interprets simple information by looking at visuals. (For example in a picture of a garden the child looks at different flowers and draws inference that flowers of a certain colour are more).
• develops the concept of zero
Class II
The learner
• works with two digit numbers
––reads and writes numerals for numbers up to 99
––uses place value in writing and comparing two digit numbers.
––forms the greatest and smallest two digit numbers (with and without repetition of given digits)
––solves simple daily life problems/situations based on addition of two digit numbers
––solves daily life situations based on subtraction of two digit numbers
––represents an amount up to Rs.100 using 3-4 notes and coins (of same/ different denominations of play money
• describes basic 3D and 2D shapes with their observable characteristics
––identifies basic 3D-shapes such as cuboid, cylinder, cone
and sphere by their names
––distinguishes between straight and curved lines
––draws/ represents straight lines in various orientations
(vertical, horizontal, slant)
• estimates and measures length/distances and capacities of containers using uniform non-standard units like a rod/ pencil, cup/ spoon/bucket etc.
• compares objects as heavier/lighter using simple balance.
• identifies the days of the week and months of the year
• sequences the events occurring according to their duration in terms of hours/days; for example, Does a child remain in school for a longer period than at home?
• draws inference based on the data collected such as the number of vehicles used in Samir’s house is more than that in Angelina’s.
Class III
The learner
• works with three digit numbers
––reads and writes numbers up to 999 using place value
––compares numbers up to 999 for their value based on their place value
––solves simple daily life problems using addition and subtraction of three digit numbers with and without regrouping, sums not exceeding 999
––constructs and uses the multiplication facts (tables) of 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 in daily life situations
––analyses and applies an appropriate number operation in the situation/context
––explains the meaning of division facts by equal grouping/
sharing and finds it by repeated subtraction. For example, 12÷3 can be explained as number of groups of 3 to make 12 and finds it as 4 by repeatedly subtracting 3 from 12
• adds and subtracts small amounts of money with or without regrouping
• makes rate charts and simple bills
• acquires understanding about 2D shapes
––identifies and makes 2D-shapes by paper folding , paper cutting on the dot grid, using straight lines etc.
––describes 2D shapes by the number of sides, corners and diagonals. For example, the shape of the book cover has 4
sides, 4 corners and two diagonals
Module
8
––fills a given region leaving no gaps using a tile of a given shape
• estimates and measures length and distance using standard units like centimetres or metres and identifies relationships
• weighs objects using standard units– grams and kilograms using simple balance
• compares the capacity of different containers in terms of non-standard units
• adds and subtracts measures involving grams & kilograms in life situations
• identifies a particular day and date on a Calendar
• reads the time correctly to the hour using a clock/watch
• extends patterns in simple shapes and numbers
• records data using tally marks, represents pictorially and draws conclusions.
Class IV
The learner
• applies operations of numbers in daily life
––multiplies 2 and 3 digit numbers
––divides a number by another number using different methods like — pictorially (by drawing dots), equal grouping or repeated subtraction and by using inter-relationship between division and multiplication
––creates and solves simple real life situations/problems including money, length, mass and capacity by using the four operations
• works with fractions
––identifies half, one-fourth, three-fourths of a whole in a given picture by paper folding and also in a collection of objects.
––represents the fractions as half, one-fourth and three fourths by using numbers/numerals
––shows the equivalence of a fraction with other fractions
• acquires understanding about shapes around her/him
––identifies the centre, radius and diameter of the circle
––finds out shapes that can be used for tiling
––makes cube/cuboids using the given nets
––shows through paper folding/paper cutting, ink blots, etc.
the concept of symmetry by reflection
8––draws top view, front view and side view of simple objects
• explores the area and perimeter of simple geometrical shapes (triangle, rectangle
• square) in terms of given shape as a unit. For example, the number of books that can completely fill the top of a table.
• converts metre into centimetre and vice-versa
• estimates the length of an object/distance between two locations, weight of various objects, volume of liquid, etc., and verifies them by actual measurement
• solves problem involving daily life situations related to length, distance, weight, volume and time involving four basic arithmetic operations
• reads clock time in hour and minutes and expresses the time in a.m. and p.m.
• relates to 24-hr-clock with respect to 12 hr-clock
• calculates time intervals/duration of familiar daily life events by using forward or backward counting/addition and subtraction
• identifies the pattern in multiplication and division (up to multiple of 9)
• observes, identifies and extends geometrical patterns based on symmetry
• represents the collected information in tables and bar graphs and draws inferences from these
Class V
The learner
• works with large numbers
––reads and writes numbers bigger than 1000 being used in her/his surroundings
––performs four basic arithmetic operations on numbers beyond 1000 by
––understanding of place value of numbers
––divides a given number by another number using standard algorithms
––estimates sum, difference, product and quotient of numbers and verifies the same using different strategies like using standard algorithms or breaking a number and then using operation. For example, to divide 9450 by 25, divide 9000 by 25, 400 by 25, and finally 50by 25 and gets the answer by adding all these quotients.
• acquires understanding about fractions
––finds the number corresponding to part of a collection
––identifies and forms equivalent fractions of a given fraction
––expresses a given fraction 1/2, 1/4, 1/5 in decimal notation and vice-versa. For example, in using units of length and money– half of Rs.10 is Rs.5
––converts fractions into decimals and vice versa
• explores idea of angles and shapes
––classifies angles into right angle, acute angle, obtuse angle and represents the same by drawing and tracing
––identifies 2D shapes from the immediate environment that have rotation and reflection symmetry like alphabet and shapes
––makes cube, cylinder and cone using nets designed for this purpose
• relates different commonly used larger and smaller units of length, weight and volume and converts larger units to smaller units and vice-versa
• estimates the volume of a solid body in known units like volume of a bucket is about 20 times that of a mug
• applies the four fundamental arithmetic operations in solving problems involving money, length, mass, capacity and time intervals
• identifies the pattern in triangular number and square number
• collects data related to various daily life situations, represents it in tabular form and as bar graphs and interprets it.
Students face more challenge to learn number sense and number operations than other maths concepts. There is urgency in Shifting learning these foundation skill from algorithm based approach to real understanding with mathematization of thoughts.
To accomplish these broaden learning outcome as per NCERT classroom teaching –learning process need resource material suited to aims and pedagogy. In primary classes one of prime objective of maths teaching is to develop interest in doing ,talking, playing maths in relation to their daily life.
Teaching learning material classified into following domain-
1. Physical classroom – wall painting , charts, display boards, benches, stationaries etc. all should be child friendly and align to aims of goal and objective of primary education.
2. Puzzles and Games- Classroom should be filled with age appropriate and level appropriate games and puzzles which seek interests of all students of class.
3. Content appropriate- TLM should be in accordance of class level content.
4. Pedagogy appropriate- TLM should be focusing class appropriate pedagogy.
Following are Teaching Learning Material for primary classes :- ( Maths 1 to 5)
(Maths kit for Primary classes)
1. Rangometry –Rangometry is a real treasure trove for children. Here shapes and colours combine together to form beautiful rangoli patterns. And also hidden in them is a whole world of geometry.
For 1st to 5th

Concept:
SHAPES AND PATTERNS
• Angles
• Shapes
• Patterns
• Geometrical problem solving
Rangometry – For 4 children
Protractor – 1 per child
In Rangometry there are eight different shapes-
Hexagon
Trapezium
Small Rhombus
Big Rhombus
Equilateral Triangle
Isosceles Triangle
Square
Rectangle
Examples of activity with Rangometry-
1. Make design of your choice /Free play
2. Manipulating Shapes
3. Counting with Meaningful purpose
4. Make your own figure and count
5. Patterns
6.Shapes from shapes
7. One shape from Different shapes
8. Comparisons of angles
2. Tangram – An exciting and challenging game to keep you questioning, exploring and discovering for hours.
For 1st to 5th

Concept:
SHAPE, SHAPE SENSE AND
SPATIAL UNDERSTANDING
• Creating shapes using Tangram pieces and developing spatial sense
• Matching the properties of two 2-D shapes by observing their sides and
corners (vertices)
• Different types of triangles
• Recognition of shapes in different orientations
• Recognizing 2-D shapes by their sides and corners
SHAPES & AREA
• Exploring similar triangles
• Area relationships between different types of shapes
• Relationship between different 2-D shapes The classical Chinese puzzle
contains 50
– 7 tangram pieces
– Booklet showing twin tangrams, convex shapes as well as usual pictures
classified according to subject
– Two sheets for introducing tangram to young children
This product is also used in Middle classes.
1 per child/ age 3 years and above
Tangram is an exciting game which stimulates creativity and which can be played either by one person or by group. The oldest known mechanical puzzle, it is Chinese in origin, but has gained popularity the world over. The 7 pieces can be arranged with tremendous geometric insight to form over 1600 shapes. A predecessor of Soma cube , the Tangram is essentially a dissection of a square.
Many different shapes are shown below. Arrange the pieces to form shapes similar to each of them.
3. Jodo blocks-

Concept:
Developing a sense of numberness, counting and operations of numbers, Searching for patterns in different ways of splitting a number, Addition and subtraction facts, Odd and Even numbers with their properties
• Area, perimeter,
volume
• Commutativity, Distributivity
• Understanding squares and cubes geometrically and in terms of numbers.
• Algebraic identities
• Factors, prime numbers, HCF, LCM
• Patterns
Counting and
Number Sense
• Recognizing colors
• Classifying on the basis of colors
• Making patterns
• Counting
• One to One correspondence
• Comparing numbers
Description:
Snap-on cubes
which can be connected on all the six sides. Useful for teaching area,
perimeter, multiplication, odd numbers, even numbers, square numbers, cube
numbers, algebra etc.
This product is also used in Primary and Middle classes.
For 4 children / age 2-16 years
These colourful blocks are fantastic multipurpose blocks that can function in myriad ways as a teaching aid and as a toy. Little one seem to be fascinated with making long long chains of blocks by choosing the colours which they find attractive. Children also start making patterns in the long trains as they make usually by a 1-1pattern by alternating the colours. After some tine children start making objects that they see around them- objects such as houses and tables. It is not just a question of improving the hand-eye co-ordination but also of giving a flight to their imagination.
Counting and colour could also be integrated with giving blocks to children for free play.
Developing number sense – Children need a lot of opportunities to count with unstructured materials in a meaningful way.
Addition and subtraction- Addition of numbers goes through different stages. Children understand addition first within a story or in some other meaningful context with the support of objects. Then it is done with focus on objects and only then with bare numbers. Children can understand important transition and is called transition from counting –all to counting –on.
Addition and Subtraction facts , Odd even , Games .
4. Jodo straw –

Jodo kit consist of connector, a vectorial connector vertex (nexor in short)whose arms can be bent to take any direction in space. The straw are all the same length. If we wish can cut different lengths with scissors. To fit the straw into the nexor, hold the nexor in one hand. Insert the arm of the nexor into the straw, and gently push the nexor into straw. We can start by making the five perfect shapes- Tetrahedron, Cube, Dodecahedron , Octahedron, Icosahedron. We can make with these straw Angles (type of angles) ,Triangles, Quadrilaterals ( Rectangle , Parallelogram, Rhombus, Trapezium, Kite) , Pentagon and Hexagon. Pyramids (square pyramid, Triangular pyramid, Pentagonal pyramid, Hexagonal Pyramid , Octagonal Pyramid.
Note: To make Hexagonal pyramids, Septagonal, Octagonal etc., You will have to shorten the base straws by cutting them with a scissors.
Prism and Anti Prisms ( triangular prism, square prism , pentagonal prism, hexagonal prism, triangular antiprism ,square antiprism , pentagonal antiprism)
Double Pyramids ( double pyramid, square double pyramid , pentagonal double pyramid)
Rhombic dodecahedron and Cuboctahedron
Note- When we count number of faces, vertices, sides for each shape , in each case
F+V = E+2
This formula is called Euler formula. While Descartes may have discovered the formula first, it was Euler had a crucial insight.
5. Digit card :-

Concept:
PLACE VALUE
• Expanding a number with respect to place value
• Comparing numbers
• Forming greatest and smallest numbers using given digits
• Reading and writing multi-digit numbers
Description:
A set of 108 cards to make 3-digit and 4-digit numbers in a game context. Helps to internalize the meaning of place-value. The game involves multiple strategies and can be enjoyed by adults also.
For 4 children/ age 7 years and above
6. Diens block

Concept:
• Algebraic
Identities and factorization
• Measurement
• Area
• Volume
• Weight
• Place Value
Description:
Contains 100 units (small cubes), 20 tens (rods), 5 hundreds (plates) and 1 thousand (large cube). Blocks for teaching volume, area and weight. Each small cube weighs 1 gram and has a volume of one cubic centimetre and one surface of 1 square centimetre. Can also be used for teaching either whole number or decimals place-value and related operations and for algebra.
For 4 children/ age 6-14 years
7. Ganit mala

Concept:-
NUMBER SENSE AND OPERATIONS FROM 0-100
• Doing
structured counting by using patterns of tens
• Grouping objects into tens and ones
• Extending patterns in sequence of numbers
• For patterns in different ways of splitting a number
• Identifying the position of numbers
MENTAL ARITHMETIC
• Addition and subtraction of 2-digit numbers mentally
Description:
For whole class use to support development of Number Sense up to 100. To learn
the position of numbers and to structure numbers. This helps to do mental
addition and subtraction up to 100.
1 per section
8. Maan card

Concept:
Place Value
• Expanded notation of a number
• Quantity sense
Description:
Also known as Gattegno cards. Consist of sets of units, tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands and lakhs cards to make up to any 6 digit number. Helps children to develop quantity value of the numbers on the basis of expanded notation.
1 per child / age 6-11 years
9. Aakar Parivar

Concept:
Shapes and Seriation
Ordering of shapes on basis of size
Visualizing and imagining shapes in objects around
Making stories
Classifying on the basis of size, color and shape
Counting
Developing and using vocabulary related to spatial relationship (Top, Bottom, Near, Far etc.)
Recognizing colors
Description:
Five shapes (circle, semicircle,
triangle, square and rectangle) in five colors with each in a set of five sizes
ranging from 2.5 cm to 12.5 cm.
This product is also used in Primary classes.
For 3-4 children / Age 2-7 years
10. Currency

Concept:
MONEY
• Identifying currency – notes and coins
• Using different combinations to make the same amount of money
• Converting Rupees to paisa
• Adding and subtracting bills
Description:
10 notes each of Rs.1000, Rs.500, Rs.100, Rs.50, Rs.20 and 100 notes each of Rs.10 and Re.1 and 10 coins each of Rs.5, Rs.2 & Re.1
For 5-6 children / age 8-12 years
11. Decimal kit

Concept:
DECIMALS & DECIMAL OPERATIONS
• Introduction of decimals
• Associating decimal fractions with decimals
• Understanding decimal place value
• Adding and subtracting of decimal Numbers
Description:
A hands-on kit for children to understand and visualize decimals in relationship with decimal-fractions. Includes games to consolidate the meaning of decimal notation. Also to compare, order, add and subtract decimals. (Contains 1 Large Cube, 20 Plates, 20 Rods, 20 Small Cubes, 3 sets of Cards and 3 Wooden Dice). Appropriate for Mathlabs and class kits (1 kit for 4 children).
This product is also used in Middle classes.
For 4 children/ age 9-13 years
12. Decimal Maan card

Concept:
DECIMALS & DECIMAL OPERATIONS
• Expressing a given fraction in decimal notation
• Understanding decimal numbers in their expanded form
• Quantity understanding of decimal numbers
Description:
Place value cards for decimals from units up to 3 decimal places.
This product is also used in Middle classes.
1 per child
13. Geo board
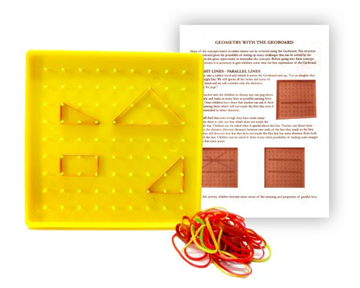
Concept:
SHAPES &
SPATIAL UNDERSTANDING
• Open and closed figures
• Concept of triangle, quadrilateral and polygon on the basis of side
• Properties of polygons and circles
– Gets the feel of an angle through observation
– Identifies right angles
– Classifies angles into right, acute and obtuse angles
– Represents right angle, acute angle and obtuse angle by drawing & tracing
• Explores intuitively rotations and reflections of familiar 2-D shapes
Description:
Square plastic board with pins to understand geometric properties of polygons and Circles.
This product is also used in Middle classes.
For 1-2 children/ age 6 years and above
14. Fraction kit

Concept:
FRACTIONAL NUMBERS
• Identification of half, one fourth and three-fourths of a whole
• Meaning of unit fractions and recognition of their symbols
• Understanding meaning of denominator
• Comparison of unit fractions
– Equivalence of 2/4 and ½ and of 2/2, 3/3, 4/4 and 1
• Addition and subtraction of like fractions
Description:
Two sets of five circular unit
fraction cut-outs ranging from ½ to 1/8
One set of 1/12 to 1/18
One Whole – a full circle
Fraction dice
Fraction cards – 5 unit fractions and 16 non-unit fractions
Appropriate for Mathlabs and class kits. This product is also used in Middle
classes.
For 4 children / age 8-13 years
15. Math mat

Awesome post! Keep up the great work! 🙂
Thanks a lot , keep support